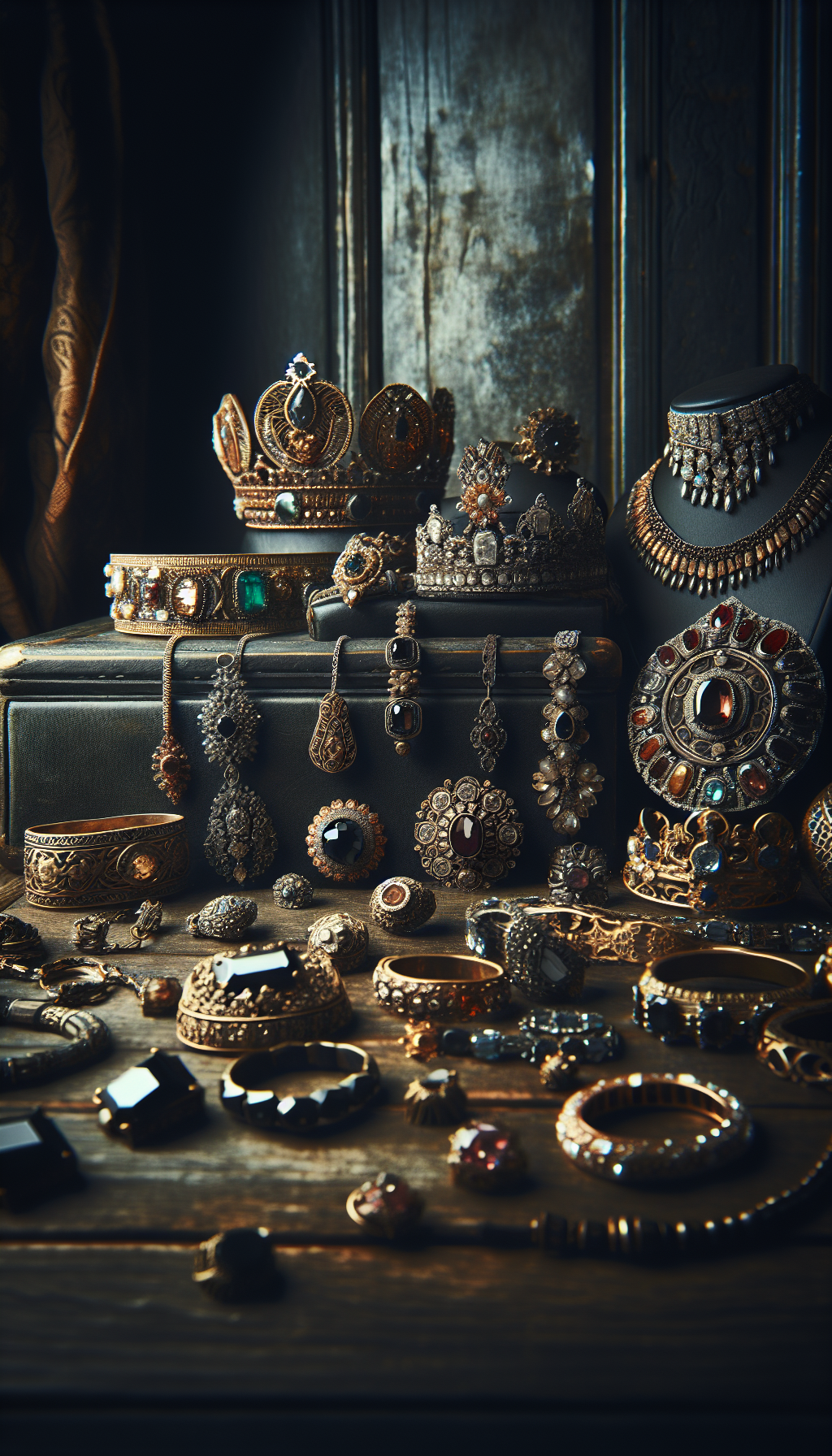
Introduction to Pre-Columbian Art Valuation
Pre-Columbian art encompasses the visual arts of indigenous peoples of the Americas created prior to European contact in 1492. These artifacts represent thousands of years of rich cultural history across diverse civilizations including the Maya, Aztec, Inca, and numerous other cultures spanning from North America to South America.
Today, these artifacts command significant interest from collectors, museums, and investors worldwide. Understanding their value requires knowledge of authenticity markers, cultural context, condition assessment, and market dynamics.
This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the complex world of Pre-Columbian art valuation, whether you’re a beginning collector or looking to appraise a family heirloom.
Understanding Pre-Columbian Art Categories
Pre-Columbian art can be categorized by culture, time period, medium, and function. The primary categories that drive valuation include:
Ceramic Artifacts
Pottery represents the most common form of Pre-Columbian art in the market. These items include:
- Figurines depicting humans, deities, and animals
- Vessels for ritual and everyday use
- Funeral urns and ceremonial pottery
- Stamps, whistles, and other ceramic objects
Stone Sculptures
Stone carvings range from monumental sculptures to portable objects:
- Masks and ceremonial objects
- Statues of deities and important figures
- Relief carvings and architectural elements
- Jade and other precious stone carvings
Precious Metal Works
Gold, silver, and copper artifacts command premium prices:
- Personal adornments (jewelry, pendants, ear spools)
- Ceremonial masks and figurines
- Religious objects and temple decorations
Textiles and Organic Materials
Though less common due to preservation challenges:
- Woven textiles (when preserved in dry environments)
- Wooden objects, tools, and ceremonial items
- Featherwork, shell art, and composite materials
Price Determinants for Pre-Columbian Art
Authenticity
Authenticity is the foremost concern in Pre-Columbian art valuation. The market is flooded with reproductions and forgeries ranging from tourist souvenirs to sophisticated fakes. Verified authentic pieces command substantially higher prices.
Provenance
A documented history of ownership significantly impacts value:
- Pre-1970 provenance is particularly valuable (preceding UNESCO Convention)
- Museum deaccession provides strong authentication
- Famous collection association increases desirability
- Clear export documentation ensures legal status
Condition
The physical state of an artifact heavily influences its value:
- Complete, unrestored pieces command premium prices
- Professional conservation may preserve value
- Extensive repairs generally decrease value
- Natural patina is preferred over cleaned surfaces
Rarity and Cultural Significance
Pieces with exceptional characteristics stand out in the market:
- Unusual iconography or artistic innovation
- Connection to important historical events or figures
- Exceptional craftsmanship or aesthetic merit
- Rare survival from less-documented cultures
Pre-Columbian Art Value Ranges
General price ranges for authentic Pre-Columbian art (2023 market values)
Authentication of Pre-Columbian Art
Scientific Testing Methods
Modern authentication often employs scientific analysis:
- Thermoluminescence (TL) testing for ceramics (dates firing)
- Carbon-14 dating for organic materials
- X-ray fluorescence to analyze material composition
- Microscopic analysis of tool marks and wear patterns
Visual Authentication Indicators
Experienced collectors and dealers look for:
- Appropriate patina and surface wear consistent with age
- Evidence of ancient tool marks and manufacturing techniques
- Culturally accurate design elements and iconography
- Natural aging consistent with burial conditions
Red Flags for Potential Forgeries
Be wary of pieces that show:
- Artificially aged surfaces (applied patina)
- Modern tool marks or manufacturing techniques
- Inconsistent iconography or cultural elements
- Unnaturally clean or perfectly preserved surfaces
- Reluctance by sellers to provide provenance information
Pre-Columbian Authentication Checklist
Use this checklist to evaluate potential authenticity markers
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Proper patina consistent with burial environment</span>
</li>
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Tool marks consistent with pre-industrial techniques</span>
</li>
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Material composition appropriate for region and period</span>
</li>
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Iconography consistent with established cultural patterns</span>
</li>
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Provenance documentation predating 1970 UNESCO Convention</span>
</li>
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Scientific testing results (TL dating, etc.) if available</span>
</li>
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Evidence of appropriate soil deposits from burial</span>
</li>
<li class="condition-checklist__item">
<input type="checkbox" disabled aria-hidden="true">
<span>Natural wear patterns consistent with age and use</span>
</li>
The Pre-Columbian Art Market
Current Market Trends
The Pre-Columbian art market shows several notable patterns:
- Increasing specialization with collectors focusing on specific cultures
- Growing premium for pieces with well-documented provenance
- Stronger performance for museum-quality items
- Greater scrutiny regarding authenticity and legal status
- Price resilience for exceptional pieces despite fluctuating markets
Key Market Venues
Pre-Columbian art is traded through various channels:
- Major auction houses (Sotheby’s, Christie’s, Bonhams)
- Specialized dealers and galleries
- Online platforms (Artsy, 1stDibs)
- Regional auctions in areas with strong collector bases
- Private sales and collector networks
Recent Notable Sales
These significant auction results demonstrate the high-end market:
Notable Pre-Columbian Art Auction Results
Recent significant sales highlighting top-tier market values
| Category | Price | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Common Ceramic Vessels | $300-$3,000 | Typical pottery with standard designs, good condition |
| Elaborate Figurines | $1,000-$10,000 | Detailed ceramic figures, exceptional preservation |
| Stone Sculptures | $2,000-$25,000+ | Size, culture, and quality dependent |
| Jade and Precious Stone Items | $3,000-$100,000+ | Museum-quality jade pendants, masks, or ceremonial items |
| Gold Artifacts | $5,000-$500,000+ | Intricate ceremonial items or high-value jewelry |
| Museum-Quality Masterpieces | $100,000-$1,500,000+ | Exceptional provenance, cultural significance, rarity |
Cultural and Regional Value Differences

Maya Artifacts
Maya art, particularly from the Classic Period (250-900 CE), typically commands premium prices:
- Intricately carved jade pendants and masks
- Polychrome ceramic vessels with narrative scenes
- Limestone reliefs and architectural elements
- Codex-style painted ceramics
Aztec and Teotihuacan Works
Central Mexican artifacts hold strong collector interest:
- Stone sculptures with distinctive iconography
- Teotihuacan masks and figurines
- Ritual objects connected to religious practices
- Artifacts with calendrical or astronomical significance
Inca and Andean Cultures
South American artifacts with distinctive characteristics:
- Gold and silver works with exceptional craftsmanship
- Textiles with geometric designs (when preserved)
- Stone vessels and architectural elements
- Ceremonial items reflecting Andean cosmology
Lesser-Known Cultures
Artifacts from these cultures often represent good value for collectors:
- West Mexican ceramics (Colima, Jalisco, Nayarit)
- Intermediate Area pieces (Costa Rica, Panama)
- North Andean cultures (Moche, Chimú)
- South American lowland artifacts
Evolution of Pre-Columbian Art Valuation
- 1850-1920
Early Collecting Era
Western museums and wealthy collectors acquire Pre-Columbian artifacts with minimal regulation. Scientific expedition discoveries drive interest.
- 1920-1960
Aesthetic Appreciation Period
Modernist artists discover Pre-Columbian aesthetics. Growing museum collections and exhibitions increase public awareness and market values.
- 1970
UNESCO Convention
UNESCO Convention on cultural property establishes international framework for protecting archaeological heritage. Provenance becomes crucial for legal trade.
- 1980-2000
Market Maturation
Major auctions establish price benchmarks. Scientific authentication becomes standard. Museums repatriate questionable acquisitions.
- 2000-Present
Digital Era Market
Online platforms expand collector base. Legal scrutiny intensifies. Established provenance commands significant premium. Museum-quality pieces reach record prices.
Legal Considerations for Collectors
International Regulations
Several international agreements impact Pre-Columbian art:
- 1970 UNESCO Convention prohibits illicit import/export of cultural property
- UNIDROIT Convention (1995) addresses international returns of cultural objects
- Bilateral agreements between source countries and market countries
Country-Specific Restrictions
Different nations have varying approaches:
- Most Latin American countries claim ownership of all archaeological materials
- The United States restricts imports through bilateral agreements
- European markets may have different enforcement practices
- Source countries actively pursue repatriation of significant pieces
Documentation Requirements
Essential paperwork for legal ownership:
- Clear provenance showing ownership history before 1970
- Export permits from country of origin (if applicable)
- Import documentation showing legal entry
- Sales receipts and authenticity certificates
Building a Legal Collection
Ethical approaches for modern collectors:
- Focus on pieces with documented pre-1970 provenance
- Purchase from established dealers with strong reputations
- Consider museum deaccessions with clear documentation
- Consult with specialized legal experts before major acquisitions
Collection Care and Value Preservation
Environmental Considerations
Optimal conditions for preserving Pre-Columbian artifacts:
- Stable temperature (65-70°F/18-21°C)
- Controlled humidity (45-55% relative humidity)
- Limited light exposure, especially UV light
- Vibration-free display and storage
- Protection from dust and pollutants
Handling and Display
Best practices for maintaining artifact condition:
- Handle minimally, using cotton gloves
- Support pieces fully when moving
- Display on stable mounts designed for specific items
- Rotate displayed items to limit light exposure
- Secure pieces from accidental impact
Conservation Approaches
When intervention becomes necessary:
- Consult professional conservators with archaeological expertise
- Document condition before any treatment
- Favor minimal, reversible interventions
- Maintain records of all conservation work
- Distinguish between conservation (stabilization) and restoration (aesthetic intervention)
Documentation and Record Keeping
Essential practices for collection management:
- Maintain detailed provenance documentation
- Photograph pieces from multiple angles
- Record dimensions, weight, and condition details
- Keep authentication certificates and scientific test results
- Document insurance appraisals and valuation updates
Tips for Collectors
For Beginning Collectors
Entry strategies for new enthusiasts:
- Educate yourself through museum visits, reference books, and auction catalogs
- Start with lower-priced, well-documented pieces from established dealers
- Focus on a specific culture, region, or type to develop expertise
- Join collector groups and attend museum events to build knowledge
- Consider common ceramic pieces with clear authenticity indicators
For Experienced Collectors
Advanced strategies for collection development:
- Focus on highest quality examples within your specialty
- Consider expanding into related but less collected areas
- Prioritize provenance over superficial aesthetics
- Build relationships with museum curators and experts
- Consider commissioned authentication studies for significant pieces
Collection Documentation
Building a professional record of your collection:
- Create detailed catalog entries for each piece
- Maintain digital and physical documentation files
- Record market comparables for insurance purposes
- Consider publishing your collection to establish ownership record
- Plan for long-term preservation through clear instructions
Investment Considerations
Understanding the financial aspects of collecting:
- View collecting primarily as cultural preservation rather than investment
- Recognize that the highest-quality pieces typically appreciate most consistently
- Budget for proper insurance, storage, and occasional conservation
- Consider the ethical and cultural implications of your collecting focus
- Plan for the eventual disposition of your collection
External Resources for Pre-Columbian Art Collectors
Sotheby's Pre-Columbian Art Department
Auction results, upcoming sales, and market information from one of the leading auction houses for Pre-Columbian art.
Christie's Pre-Columbian Art Collecting Guide
Comprehensive collector's guide with authentication tips, market insights, and expert advice from Christie's specialists.
Pre-Columbian Art on Artsy
Online marketplace featuring Pre-Columbian artifacts from reputable galleries with pricing information.
Sands of Time Gallery
Specialized dealer offering authenticated Pre-Columbian artifacts with detailed descriptions and pricing.
Maya Archaeology - Legal Notice
Important information regarding legal considerations and antiquities laws for Maya artifacts.
ValueMyStuff Pre-Columbian Art Appraisals
Professional appraisal service specializing in Pre-Columbian artifacts for insurance and market value.
Edgar L. Owen Galleries
Established gallery specializing in Pre-Columbian artifacts from various cultures with educational information.
Common Questions About Pre-Columbian Art Value
How much is pre-Columbian pottery worth?
Pre-Columbian pottery values vary widely based on authenticity, condition, culture of origin, age, and artistic merit. Basic, undecorated authentic vessels might start around $300-500, while nicely decorated figurines can range from the mid-hundreds to several thousand dollars. Museum-quality examples with exceptional artistry or cultural significance can command tens of thousands of dollars. For example, a basic Colima vessel might sell for $500-1,000, while an elaborate Maya polychrome vase with detailed narrative scenes could fetch $5,000-15,000 or more at specialized auctions. Values increase significantly for pieces with documented pre-1970 provenance.
How can I authenticate Pre-Columbian art?
Authentication of Pre-Columbian art involves multiple approaches:
1. **Scientific testing**: Thermoluminescence (TL) dating for ceramics, which measures time since firing; radiocarbon dating for organic materials; and material composition analysis.
2. **Provenance research**: Documented ownership history, especially predating the 1970 UNESCO Convention.
3. **Stylistic analysis**: Evaluation by experts familiar with the specific cultural styles, iconography, and manufacturing techniques.
4. **Physical examination**: Assessment of appropriate aging, tool marks, wear patterns, and material properties consistent with ancient production.
For valuable pieces, consulting with specialized authentication laboratories, museum curators, or established dealers with decades of experience is recommended. Be wary of pieces without clear provenance or those that appear too perfect or clean.
Is it legal to own Pre-Columbian art?
The legality of owning Pre-Columbian art depends on several factors:
1. **Provenance**: Items with documented history showing they left their country of origin before 1970 (when the UNESCO Convention was established) are generally legal to own in most countries.
2. **Country-specific laws**: Some artifacts may be legal in one country but illegal in another due to bilateral agreements between nations. For example, the United States has agreements restricting imports of archaeological materials from many Latin American countries.
3. **Type of artifact**: Some particularly significant categories of artifacts may have specific restrictions.
It's important to note that most Latin American countries consider undocumented archaeological materials to be national property. Maya pottery from Guatemala's Peten region is especially regulated. For legal collecting, focus on pieces with documented pre-1970 provenance, proper export documentation, or items from old museum or documented private collections.
What are the characteristics of Pre-Columbian art?
Pre-Columbian art exhibits diverse characteristics that vary by culture and period:
1. **Iconography**: Distinctive symbolic imagery often depicting deities, rulers, natural forces, and cosmic concepts. Many cultures used standardized motifs and symbols with specific meanings.
2. **Materials**: Use of local materials including clay, stone (jade, obsidian, limestone), metals (gold, silver, copper), and organic materials (feathers, shells, textiles).
3. **Stylistic elements**: Often features formalized, abstract representations rather than naturalism. Maya art tends toward narrative scenes, while Aztec art often employs geometric symmetry.
4. **Technological aspects**: Demonstrates sophisticated techniques despite pre-industrial tools, including lost-wax casting, stone carving without metal tools, and complex ceramic firing methods.
5. **Cultural purposes**: Most pieces served ritual, religious, political, or funerary functions rather than purely decorative purposes.
These distinctive characteristics help experts authenticate pieces and assign them to specific cultures and time periods.
What factors affect the value of Pre-Columbian artifacts?
Several key factors determine the market value of Pre-Columbian artifacts:
1. **Authenticity**: Genuine ancient pieces command significantly higher prices than reproductions or heavily restored items.
2. **Provenance**: Documented ownership history, especially predating 1970, substantially increases value and ensures legal status.
3. **Condition**: Complete, well-preserved examples with minimal restoration are most desirable.
4. **Rarity**: Uncommon forms, exceptional artistic quality, or pieces from less-documented cultures may command premium prices.
5. **Cultural significance**: Items depicting important deities, historical events, or showing exceptional iconography typically attract higher interest.
6. **Material**: Gold, jade, and other precious materials generally command higher prices than ceramics or stone.
7. **Size and displayability**: Aesthetically pleasing, well-proportioned pieces that display effectively often attract collector interest.
8. **Market trends**: Collecting fashions change over time, with certain cultures or artifact types gaining or losing popularity.
Where can I sell Pre-Columbian artifacts from my collection?
If you have authentic Pre-Columbian artifacts with proper documentation, several reputable avenues exist for selling:
1. **Specialized auction houses**: Major auction houses like Sotheby's, Christie's, and Bonhams have dedicated Pre-Columbian departments for higher-value pieces.
2. **Specialized dealers**: Established galleries that focus on Pre-Columbian art, including Sands of Time, Artemis Gallery, and Edgar L. Owen.
3. **Online platforms**: For mid-range pieces, platforms like Artsy and 1stDibs connect sellers with interested buyers.
4. **Regional auction houses**: Smaller auction houses sometimes handle archaeological collections, often at lower commission rates.
Before selling, ensure you have proper documentation of provenance and authenticity. For valuable items, consider obtaining professional appraisals from multiple sources. Be prepared to provide detailed photographs and condition reports. Remember that items without clear provenance may face challenges in the legitimate market.
How should I care for my Pre-Columbian artifacts?
Proper care is essential for preserving both the condition and value of Pre-Columbian artifacts:
1. **Environmental control**: Maintain stable temperature (65-70°F/18-21°C) and humidity levels (45-55% RH). Avoid direct sunlight and fluorescent lighting, which can cause fading and deterioration.
2. **Handling**: Use clean cotton gloves when handling items. Always support objects fully, especially ceramics and fragile pieces.
3. **Display**: Use stable, padded mounts designed for each specific object. Secure items from accidental bumps or vibration.
4. **Cleaning**: Avoid cleaning artifacts yourself. Inappropriate cleaning can damage patina and surfaces, reducing both authenticity indicators and value.
5. **Storage**: When not displayed, store items in acid-free containers with appropriate padding. Keep separate inventory records with photographs.
6. **Insurance**: Obtain specialized insurance for archaeological collections with accurate valuations.
7. **Professional conservation**: For any necessary stabilization or repair, consult only with conservators experienced in archaeological materials.
Remember that original condition, including appropriate patina and wear, is valued in archaeological objects. "Improving" appearance through cleaning or restoration often decreases both authenticity and market value.
Conclusion: Building Value in Pre-Columbian Collecting
The world of Pre-Columbian art offers fascinating opportunities for collectors at all levels of experience and investment. While the market presents challenges—particularly around authentication and legal considerations—it also rewards careful research, patience, and a genuine passion for the artistic achievements of ancient American civilizations.
For collectors focusing on value, several principles should guide your approach:
Prioritize provenance: Well-documented history remains the foundation of both legal and financial value.
Focus on quality over quantity: A single exceptional piece often appreciates more than multiple average examples.
Develop specialized knowledge: Understanding the nuances of specific cultures and periods gives you competitive advantage in identifying undervalued pieces.
Build relationships: Connections with reputable dealers, auction specialists, and fellow collectors create access to better pieces before they reach the open market.
Document your collection: Professional inventory records, condition reports, and authentication studies preserve information and enhance long-term value.
Most importantly, approach collecting with respect for the cultural heritage these objects represent. The most successful collections combine financial value with educational purpose and preservation ethics, ensuring these remarkable artistic traditions continue to be appreciated and understood by future generations.
Get a Professional Appraisal
Unsure about your item’s value? Our certified experts provide fast, written appraisals you can trust.
- Expert report with photos and comps
- Fast turnaround
- Fixed, upfront pricing
No obligation. Secure upload.
| Item | Price | Date | Auction House |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maya Jade Belt Pendant | $1,575,500 | 2004 | Sotheby's |
| Olmec Blue-Green Jade Figure | $479,000 | 2019 | Christie's |
| Colima Hollow Figure Dog | $87,500 | 2021 | Bonhams |
| Maya Limestone Relief | $212,500 | 2022 | Sotheby's |
| Teotihuacan Stone Mask | $352,800 | 2020 | Christie's |